What are the common types and main functions of marine rigging shackles?
Overview of Marine Rigging Shackles
Marine rigging shackles are widely used connectors in shipbuilding, offshore engineering, port operations, and other heavy-load lifting and towing operations. They are primarily used for temporary or detachable connections between wire ropes, anchor chains, slings, or other rigging. They typically consist of a shackle body, a pin, and a fixing device. Connection and removal are achieved by rotating or inserting the pin. Because ship operations often involve humid, high-salinity, and high-load environments, marine rigging shackles must not only possess high load-bearing capacity but also corrosion resistance and reliable structural safety. They play an important role in various scenarios, including ship lifting, mooring, towing, and anchoring.
Common Types of Marine Rigging Shackles
Marine rigging shackles can be categorized into various types based on their structure, usage, and application. Common types include bow shackles, D-shaped shackles, bolt-type shackles, safety latch shackles, and swivel shackles. These shackles vary in shape, load-bearing characteristics, and operation methods to suit different operational requirements. For example, bow shackles offer greater flexibility when connecting multiple rigging pieces, while D-shaped shackles are more suitable for lifting or pulling operations with unidirectional loads.
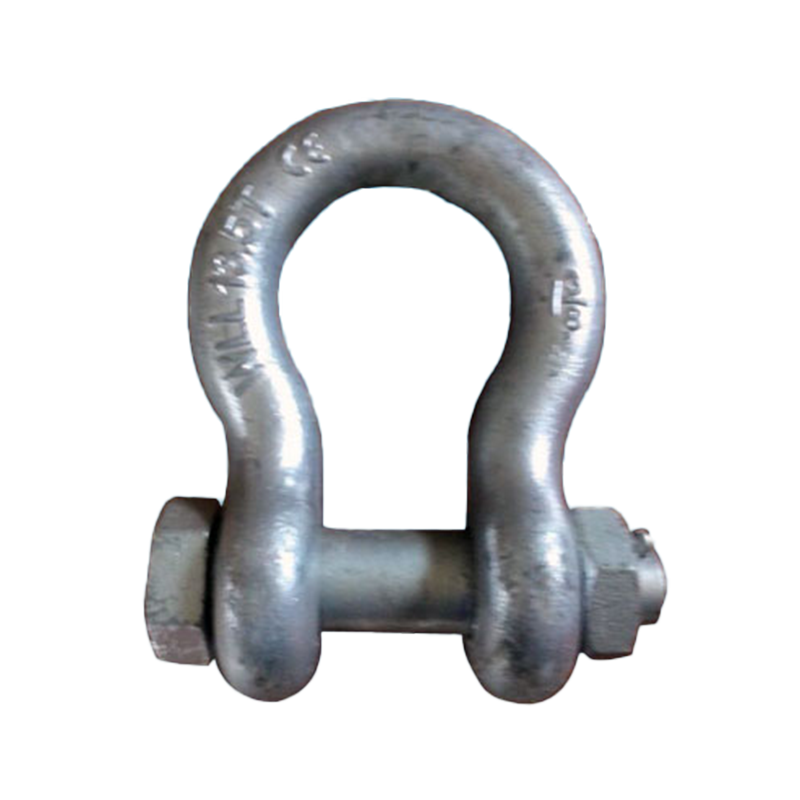
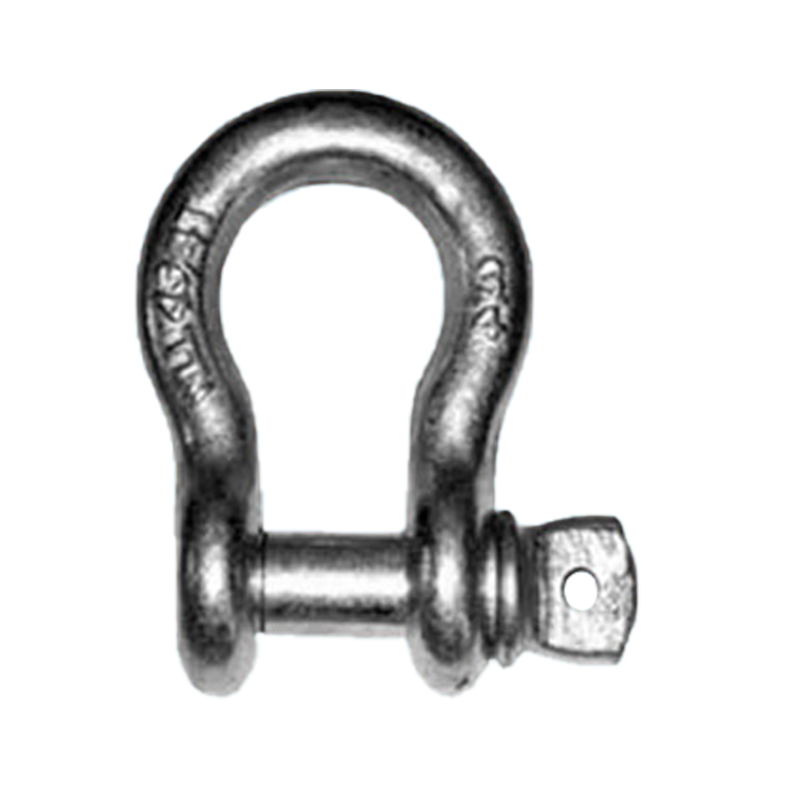
Bow Shackle
The bow shackle features an arc or nearly arc-shaped body with a wider bend, accommodating the connection of multiple rigging pieces or wire ropes. Because the arc-shaped structure distributes some of the stress when loaded, bow shackles offer greater stability under multi-directional loads and are often used in ship loading and unloading operations or mooring operations, where multiple slings need to be temporarily connected. The pin can be secured with either a threaded lock or a latch, facilitating quick assembly and disassembly in various environments.
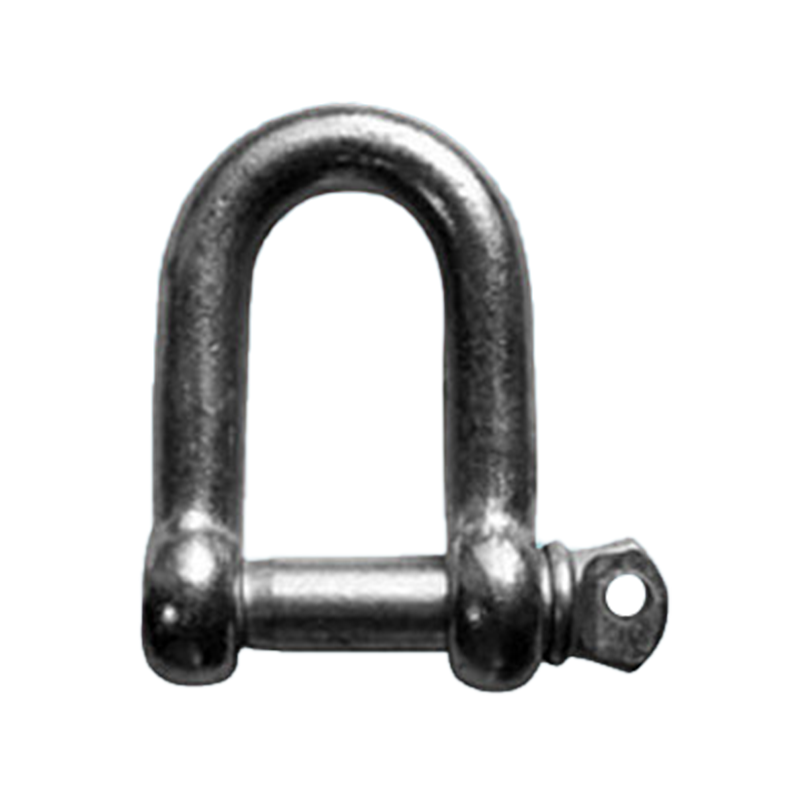
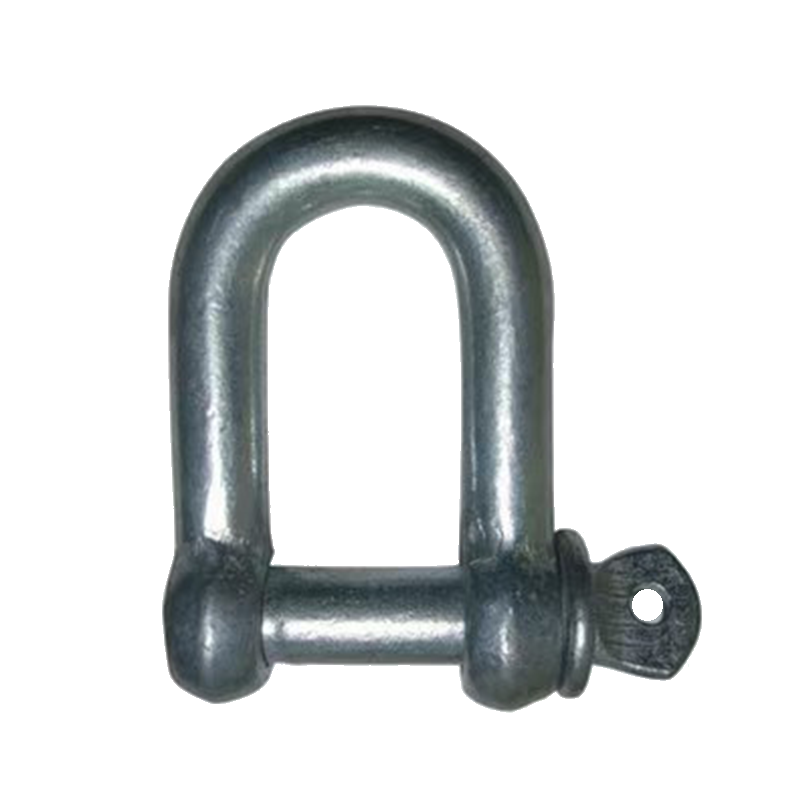
D-Shackle
The D-shaped shackle resembles the letter "D," with two long straight sides and a curved top. The load is concentrated along the long side. It is suitable for lifting and pulling operations with unidirectional loads, reducing the risk of lateral deformation of the shackle body. D-shaped shackles are typically used to connect chain links or single wire ropes, and are particularly well-suited for ship lifting operations requiring stable loads.
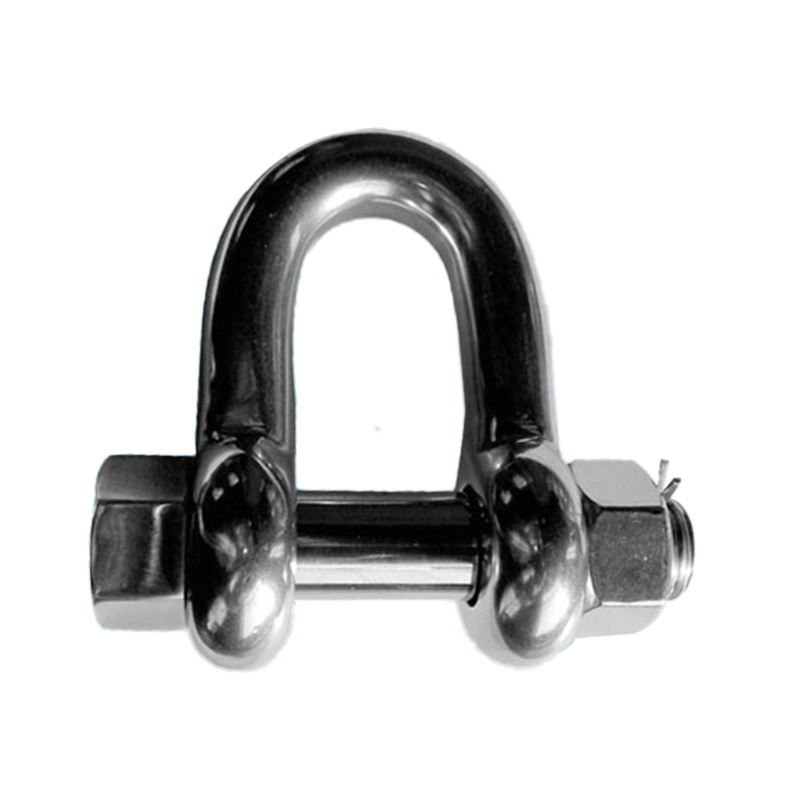
Bolt-on Shackle
A bolt-on shackle incorporates a bolt, nut, and cotter pin in a traditional latch-on design, effectively preventing the pin from loosening due to vibration or impact during operation. This design offers excellent connection stability during long-term offshore operations subject to stress and frequent vibration. It is commonly used for long-term mooring of ships, anchoring systems, and securing connections on offshore platform equipment, reducing the need for frequent inspections and tightening.
Safety-Lock Shackle
The safety-lock shackle utilizes a combination of a latch and a locking ring or spring clip, ensuring a secure connection while facilitating quick and easy removal. It is commonly used in operations requiring frequent connection changes or assembly and disassembly, such as dock loading and unloading, fishing vessel operations, and temporary lifting. The safety-lock shackle's advantage lies in its ease of operation, allowing for quick installation and removal even when wearing gloves or in wet conditions.
Swivel Shackle
The swivel shackle features a pivotable connection end, preventing entanglement of the wire rope or chain during operation. This shackle is suitable for applications requiring the prevention of torsional force accumulation, such as towing, lifting large components, or deploying and retrieving fishing gear. During ship deck operations, rotating shackles can reduce stress concentration caused by twisting in rigging, thereby extending the service life of the rigging.
The Role of Marine Rigging Shackles in Lifting and Hoisting
In ship lifting and hoisting operations, shackles are crucial for connecting hooks, slings, and the load being hoisted. They must withstand combined vertical and horizontal loads, ensuring a stable and secure connection during the lifting process. Selecting the appropriate shackle type and using it according to its rated load is crucial for preventing lifting accidents. For ships with frequent lifting operations, the appropriate shackle structure should be selected based on the load and direction of the lift to minimize fatigue damage to the shackle and rigging.
The Role of Marine Rigging Shackles in Mooring and Anchoring
During mooring and anchoring operations, shackles are used to connect cables, anchor chains, mooring rings, and other components. Their primary function is to provide a secure connection and withstand the tensile forces generated by the ship's wind, waves, and currents. Because the direction and magnitude of mooring forces can vary with changing sea conditions, bow-shaped shackles, which can accommodate multi-directional forces, are commonly used. Bolted shackles are commonly used for long-term mooring or deep-sea anchoring to improve loosening resistance and durability.
The Role of Marine Rigging Shackles in Towing Operations
Towing operations include tugboat towing, salvage operations, and buoy movement. Shackles connect towlines, wire ropes, and towed objects. Force fluctuations are significant during towing operations, especially under wave action, where transient impact forces can exceed static loads. Therefore, shackles require a high safety factor and good impact resistance. Rotating shackles play a vital role in preventing towline kinks.
The Role of Marine Rigging Shackles in Offshore Equipment Installation
During the installation of offshore platforms, floating production storage and offloading (FPSO) vessels, and offshore wind turbines, shackles serve as temporary connectors for lifting, positioning, and securing. Due to the large size and weight of these equipment, the load-bearing capacity, corrosion resistance, and operability of the shackles are particularly important. During installation, the reliability of the shackles directly impacts the positioning accuracy and efficiency of the equipment.
Maintenance and Safety Precautions
Marine rigging shackles should be protected from overloading, impact loading, and prolonged oblique forces during use. Daily inspections should focus on the shackle body and pin for wear, deformation, cracks, and corrosion, and prompt replacement if any problems are found. Shackles exposed to marine environments for extended periods should be regularly cleaned, treated for rust, and, if necessary, lubricated or coated with grease or a protective coating. The manufacturer's rated working load (WLL) and safety factor should be adhered to to ensure safety during use.
| Shackle Type |
Structural Features |
Applicable Scenarios |
| Bow Shackle |
Wide curved shape, suitable for multi-directional loads |
Multiple sling connections, mooring, cargo handling operations |
| D Shackle |
Stable under unidirectional load, reduces lateral deformation |
Single wire rope connection, lifting and hoisting |
| Bolt-Type Shackle |
Strong anti-loosening performance, suitable for long-term connections |
Long-term mooring, anchoring systems |
| Safety Pin Shackle |
Convenient disassembly, reliable locking |
Temporary lifting, fishing operations, dock cargo handling |
| Swivel Shackle |
Rotatable to prevent tangling, reduces torque |
Towing operations, fishing gear handling, rotating lifts |





 English
English 中文简体
中文简体