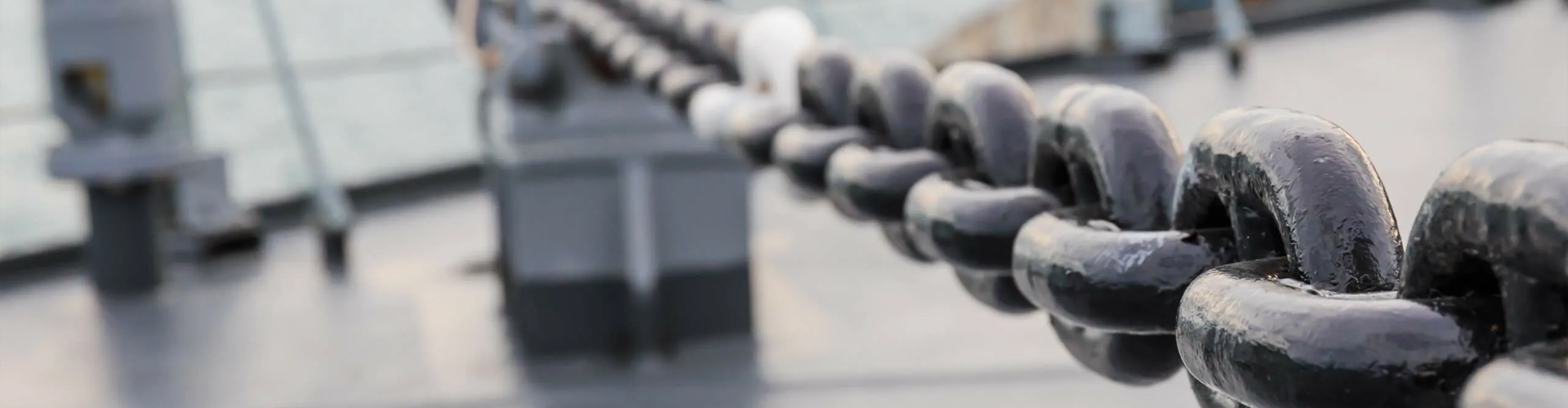
What are the daily inspection and maintenance methods for anchor chains and accessories?
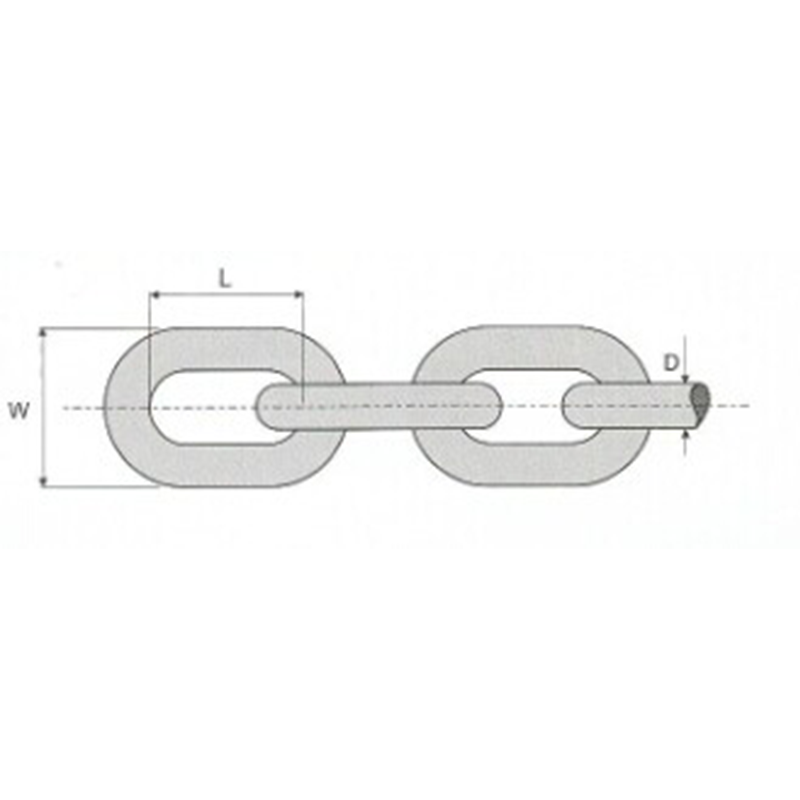
Inspect the anchor chain for surface wear and corrosion
Over long-term use, anchor chains are subject to various factors, such as seawater, sediment, and collisions, causing surface wear, corrosion, and even partial flaking. During routine inspections, the anchor chain should be rolled out section by section and surface debris removed with a steel brush or cleaning tool to inspect the underlying metal. Minor rust can be treated by sandblasting or hand polishing. If the wear depth approaches the design thickness limit for the links, the chain should be recorded and replaced as planned. Corrosion should be assessed based on the operating environment; for example, more frequent inspections are required in areas with high salinity.
Inspect the security of link connections
An anchor chain consists of multiple links and connectors, and the connections are concentrated points of stress and wear. During routine maintenance, focus on inspecting the shackles, connectors, and Kenter links to ensure that the pins, nuts, or locking devices are not loose, deformed, or broken. The gap and diameter of the connectors can be measured to determine if they meet replacement standards. If any connectors are bent or cracked, they should be removed from service and replaced immediately. A secure connection is crucial to the overall load balance and safety of the anchor chain.
Regularly measure anchor chain weight and dimensional changes
During use, anchor chain gradually loses weight due to wear and corrosion. Regularly weighing and measuring the chain link diameter allows for a visual assessment of the extent of chain wear. When weight loss or diameter reduction reaches the manufacturer's specified replacement standards, the entire length of anchor chain or the affected link should be replaced promptly. This measurement not only aids in maintenance planning but also serves as important reference data for vessel inspections to ensure safe operation.
Check the alignment of the anchor chain locker and pulley system
During retraction and retraction, the anchor chain passes through the anchor chain pulley and fairlead. If the pulley groove pattern does not match the chain link size, it may cause increased chain link wear or poor operation. During routine maintenance, check the pulley groove for smoothness, cracks, or abnormal wear, and confirm that it matches the anchor chain specifications. Ensure the chain locker is clean and free of water, and check that the drainage system is unobstructed to prevent excessive humidity from accelerating chain link corrosion.
Regularly lubricate anchor chains and movable joints
Although anchor chains cannot maintain a lubricating film while operating underwater, lubricant should be applied promptly after retrieving, cleaning, and drying the chain, especially to movable parts such as shackles, swivels, and connecting rings. Lubrication not only reduces direct metal-to-metal friction but also isolates some moisture and air, slowing the progression of corrosion. Lubricants should be selected based on the vessel's operating environment and avoid those containing ingredients that are easily washed away by seawater.
Check the alignment of the anchor chain locker and pulley system
During retraction and retraction, the anchor chain passes through the anchor chain pulley and fairlead. If the pulley groove pattern does not match the chain link size, it may cause increased chain link wear or poor operation. During routine maintenance, check the pulley groove for smoothness, cracks, or abnormal wear, and confirm that it matches the anchor chain specifications. Ensure the chain locker is clean and free of water, and check that the drainage system is unobstructed to prevent excessive humidity from accelerating chain link corrosion.
Regularly lubricate anchor chains and movable joints
Although anchor chains cannot maintain a lubricating film while operating underwater, lubricant should be applied promptly after retrieving, cleaning, and drying the chain, especially to movable parts such as shackles, swivels, and connecting rings. Lubrication not only reduces direct metal-to-metal friction but also isolates some moisture and air, slowing the progression of corrosion. Lubricants should be selected based on the vessel's operating environment and avoid those containing ingredients that are easily washed away by seawater.
Cleaning anchor chains and accessories
After each heave, the anchor chain and anchoring equipment should be rinsed with fresh water to remove deposits such as salt, silt, and seaweed. Chains with thick marine growth can be cleaned with a high-pressure water jet or mechanical brush. Cleaning is not only for aesthetic reasons but also to prevent deposits from retaining moisture and accelerating metal corrosion. For vessels that remain idle for extended periods, the anchor chain should be thoroughly dried after cleaning and properly treated with rust prevention.
Inspect the connection between the anchoring equipment and the anchor chain
The connection between the anchor chain and the anchor is a critical area subject to impact and tension, typically connected via a shackle or swivel. Daily inspections should confirm that the connection is secure, the pins are not loose, and the connection holes show no obvious wear, enlargement, or cracks. If any connection is misaligned or loose, it should be immediately reinstalled and reinforced to prevent it from falling out during anchoring or retrieval.
Develop a regular maintenance and replacement plan
Daily inspections alone cannot fully assess the health of the anchor chain. Therefore, a maintenance plan should be developed based on navigation records, frequency of use, and environmental conditions. A comprehensive inspection is recommended at regular intervals (such as six months or a year), including measuring each link, disassembling and inspecting components, and repairing the protective layer. Chain segments that have reached the end of their service life should be replaced all at once rather than individually to ensure consistent force distribution and safe operation.
Usage and Storage Precautions
During use, the anchor chain should be protected from sudden, high impact forces, such as dropping anchor without the vessel stabilized. During storage, the chain locker should be kept ventilated and dry, avoiding contact with acids and alkalines. If the anchor chain is not in use for an extended period, it should be cleaned, coated with anti-rust oil, and covered with a protective cloth. Proper usage and storage habits can reduce the stress and frequency of future maintenance.
Establish an inspection and maintenance record file
To facilitate subsequent maintenance and safety management, an inspection file should be maintained for anchor chains and accessories. This should record the time of each inspection, any defects found, the measures taken, and any replacements. This provides a complete usage history, helping to determine the wear trend and lifespan of the anchor chain, providing a basis for annual ship inspections or classification society surveys.
| Inspection Item |
Inspection Method |
Recommended Frequency |
Action Measures |
| Surface wear and corrosion |
Visual inspection after cleaning |
Once a month |
Light grinding and rust removal; replace if severe |
| Connector fastening |
Check shackle and link locking status |
Before each use |
Tighten or replace |
| Link deformation |
Measure dimensions and compare |
Once a quarter |
Replace immediately if exceeding limit |
| Protective coating integrity |
Observe for peeling or blistering |
Once a quarter |
Clean and repair coating |
| Pulley-chain compatibility |
Check pulley groove shape matches link size |
Once a quarter |
Repair or replace pulley |
| Lubrication condition |
Check grease application |
After each cleaning |
Reapply lubricant |
| Cleaning and anti-rust treatment |
Rinse with fresh water and dry |
After each use |
Apply anti-rust oil |
| Anchor-chain connection status |
Check fastening strength of connection |
Before each use |
Reinforce or replace connectors |





 English
English 中文简体
中文简体